JavaScript
Const vs Let vs Var
The const keyword in front of an object implies that there is an object, and you're working with references to alter it. It also (correctly) implies that you should not attempt to reassign references to this object.
const obj = {a: 'foo', b: 'bar'};
const obj2 = {z: 'baz'};
obj = obj2; // const will prevent this operation. const obj = {a: 'foo', b: 'bar'};
const obj2 = {z: 'baz'};
obj = obj2; // const will prevent this operation. const does not imply that the object properties should not be altered. It does imply that you should not try to change the reference. If you plan to reassign references to the object, then you use let.
- var
x++ VS ++x
let x = 1; console.log(x++);//1 return the value before operation console.log(x);//2 x = 1; console.log(++x);//2 return the value after operation, equals to the value of (x+1) console.log(x);//2 x=1; console.log(x+1);//2 console.log(x);//1
let x = 1;
console.log(x++);//1 return the value before operation
console.log(x);//2
x = 1;
console.log(++x);//2 return the value after operation, equals to the value of (x+1)
console.log(x);//2
x=1;
console.log(x+1);//2
console.log(x);//1
Type Conversion and Coercion
- Conversion
Number() String()
Number()
String()Logical Operators
== loose equal (type coercion)
!=
=== strict equal
!==
Truthy and Falsy Values
-
Falsy value:
'' or "" 0 undefined null NaN false
'' or "" 0 undefined null NaN false- NaN - Not a number
Switch statement
const day = 'monday';
switch(day){
case 'monday:
console.log('It is monday');
break;
case 'tuesday':
console.log('It is tuesday');
break;
default:
console.log('');
}const day = 'monday';
switch(day){
case 'monday:
console.log('It is monday');
break;
case 'tuesday':
console.log('It is tuesday');
break;
default:
console.log('');
}Conditional(ternary) operator
const age =23;
age >= 18 ? consol.log('Can drink alcholol') : console.log('Can not drink alcholol');const age =23;
age >= 18 ? consol.log('Can drink alcholol') : console.log('Can not drink alcholol');let age; const drink = age >= 18 ? 'alcholol' : 'non-alcholol'; console.log(drink);
let age;
const drink = age >= 18 ? 'alcholol' : 'non-alcholol';
console.log(drink);Together with template literal
- Usage of the backtick character (`) in JavaScript
${}
console.log('I drink ${age >= 18 ? 'alcholol' : 'non-alcholol'}')console.log('I drink ${age >= 18 ? 'alcholol' : 'non-alcholol'}')Array
const arr1 = ['a',1,true]; console.log(arr1[0]);
const arr1 = ['a',1,true];
console.log(arr1[0]);array method
- push: add an element to the end of an array.
const newArrLength = arr.push(element);
- unshift: add an element to the start of an array.
const newArrLength = arr.unshift(element);
- pop: remove the last element from array
const lastElement = arr.pop();
- shift: remove the first element from array
const firstElement = arr.shift();
- join:
const arr1 = [0,1,2,3];
console.log(arr1.join(''));//output: 0123
console.log(arr1.join(' '));//output: 0 1 2 3
console.log(arr1.join('.'));//output: 0.1.2.3
console.log(arr1.join('\n'));
/*output:
0
1
2
3
*/const arr1 = [0,1,2,3];
console.log(arr1.join(''));//output: 0123
console.log(arr1.join(' '));//output: 0 1 2 3
console.log(arr1.join('.'));//output: 0.1.2.3
console.log(arr1.join('\n'));
/*output:
0
1
2
3
*/- indexOf(element):
The indexOf() method returns the first index at which a given element can be found in the array, or -1 if it is not present.
const beasts = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'bison'];
console.log(beasts.indexOf('bison'));
// Expected output: 1
// Start from index 2
console.log(beasts.indexOf('bison', 2));
// Expected output: 4
console.log(beasts.indexOf('giraffe'));
// Expected output: -1
const beasts = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'bison'];
console.log(beasts.indexOf('bison'));
// Expected output: 1
// Start from index 2
console.log(beasts.indexOf('bison', 2));
// Expected output: 4
console.log(beasts.indexOf('giraffe'));
// Expected output: -1
- includes(element):
The includes() method determines whether an array includes a certain value among its entries, returning true or false as appropriate.
const pets = ['cat', 'dog', 'bat'];
console.log(pets.includes('cat'));
// Expected output: true
console.log(pets.includes('snake'));
// Expected output: falseconst pets = ['cat', 'dog', 'bat'];
console.log(pets.includes('cat'));
// Expected output: true
console.log(pets.includes('snake'));
// Expected output: falseObject
const obj1 = {arr:['a',1,true],char:'a',num:1,boolean:true};
console.log(obj1.arr);// Dot notation, output: ['a', 1, true]
console.log(obj1['num']);// Bracket Notation, output: 1
const key = 'boolean';
console.log(obj1[key]);//output: true Bracket Notation works with computed property name(a variable for example)
console.log(obj1.key);//output: undefined reason: Dot notation dosen't work with a computed property name, only takes real property name.const obj1 = {arr:['a',1,true],char:'a',num:1,boolean:true};
console.log(obj1.arr);// Dot notation, output: ['a', 1, true]
console.log(obj1['num']);// Bracket Notation, output: 1
const key = 'boolean';
console.log(obj1[key]);//output: true Bracket Notation works with computed property name(a variable for example)
console.log(obj1.key);//output: undefined reason: Dot notation dosen't work with a computed property name, only takes real property name.Function
- Funciton declaration
function calc1(){
return ;
}function calc1(){
return ;
}- Funciton expression:
Function expressions in JavaScript are not hoisted, unlike function declarations. You can't use function expressions before you create them.
const calc2 = function (){
return ;
}const calc2 = function (){
return ;
}- Arrow function: a compact alternative to a traditional function expression(not hoisted as well)
Arrow functions don't have their own bindings to this, arguments or super, and should not be used as methods.
Arrow functions don't have access to the new.target keyword.
Arrow functions aren't suitable for call, apply and bind methods, which generally rely on establishing a scope.
Arrow functions cannot be used as constructors.
Arrow functions cannot use yield, within its body.
const calc3 = (param1, paramN) => param1+paramN //expression
const calc3 = (param1, paramN) => param1+paramN //expressionScope & TDZ hoist
-
Global scope (This keyword point to window)
-
Function scope
-
Block scope (Introduced from ES6)
Example: An if statement or a for loop is a scope -
var doesn't apply to block scope
{
var str = 'hello';
const str2 = 'hello2';
}
console.log(str); // hello
console.log(str2); //Uncaught ReferenceError: str2 is not defined{
var str = 'hello';
const str2 = 'hello2';
}
console.log(str); // hello
console.log(str2); //Uncaught ReferenceError: str2 is not definedThis keyword
Used with a method: point to the object that is calling the method
Used with a simple function call: this = undefined
Used with a arrow function: this point to the surrounding of the arrow function(lexical this)
Used with Event listener: this point to DOM element that the handler is attached to
Data Structures, Modern operaters and Strings
Destructuring Arrays
let arr1 = [1,2,3]; const [x,y,z] = arr1; console.log(x,y,z); const[first, ,second] = arr1; console.log(first,second); let arr2 = ['a','b','c']; [arr1,arr2] = [arr2, arr1]; console.log(arr1); console.log(arr2); const nested = [1,2, [3, 4]]; const [a, , [c,d]] = nested; console.log(a,c,d); const [i=1,j=1,k=1] = [7,8]; console.log(i,j,k);
let arr1 = [1,2,3];
const [x,y,z] = arr1;
console.log(x,y,z);
const[first, ,second] = arr1;
console.log(first,second);
let arr2 = ['a','b','c'];
[arr1,arr2] = [arr2, arr1];
console.log(arr1);
console.log(arr2);
const nested = [1,2, [3, 4]];
const [a, , [c,d]] = nested;
console.log(a,c,d);
const [i=1,j=1,k=1] = [7,8];
console.log(i,j,k);Destructuring Objects
const restaurant = {
name:'wendys',
openningHours:'6-24',
categories:'fastFood'
};
const {name,openningHours, categories} = restaurant;
console.log(openningHours);
const {name: restaurantName,openningHours: hours, categories: tags} = restaurant;//assign key to new vraiable name
console.log(restaurantName,hours,tags);//wendys 6-24 fastFood
const {menue1, menue2 = 'burger',name: name2 = 'alternative name', categories:tag} = restaurant;
console.log(menue1,menue2,name2,tag);//undefined burger wendys fastFoodconst restaurant = {
name:'wendys',
openningHours:'6-24',
categories:'fastFood'
};
const {name,openningHours, categories} = restaurant;
console.log(openningHours);
const {name: restaurantName,openningHours: hours, categories: tags} = restaurant;//assign key to new vraiable name
console.log(restaurantName,hours,tags);//wendys 6-24 fastFood
const {menue1, menue2 = 'burger',name: name2 = 'alternative name', categories:tag} = restaurant;
console.log(menue1,menue2,name2,tag);//undefined burger wendys fastFood- Mutating variables
//Mutating variables
let a = 111;
let b = 999;
const obj = {a:2,b:8,c:14};
({a,b} = obj); // need to wrap {} into parenthesis or it won't work
console.log(a,b);//a=2,b=8//Mutating variables
let a = 111;
let b = 999;
const obj = {a:2,b:8,c:14};
({a,b} = obj); // need to wrap {} into parenthesis or it won't work
console.log(a,b);//a=2,b=8- Nested objects
//Nested objects
const hours = {fri:{open:'8', close:'17'},sat:{open:'8', close:'17'}};
const {fri:{open, close}} = hours;
console.log(open,close);//Nested objects
const hours = {fri:{open:'8', close:'17'},sat:{open:'8', close:'17'}};
const {fri:{open, close}} = hours;
console.log(open,close);- function
function orderDelivery({starter = 'soup',main,time,address}){
console.log(`This ${starter} and ${main} will be delivered to ${address} at ${time} o'clock`)
} //soup is the default value of starter
const order1 = {starter:'salad', main:'steak', time:'5', address:'Pitt'};
orderDelivery(order1);
const order2 = {main:'burger', time:'8', address:'ASU'};
orderDelivery(order2);function orderDelivery({starter = 'soup',main,time,address}){
console.log(`This ${starter} and ${main} will be delivered to ${address} at ${time} o'clock`)
} //soup is the default value of starter
const order1 = {starter:'salad', main:'steak', time:'5', address:'Pitt'};
orderDelivery(order1);
const order2 = {main:'burger', time:'8', address:'ASU'};
orderDelivery(order2);The spread operator
const arr = [3,4,5]; const arr1 = [1,2,arr[0],arr[1],arr[2]]; const arr2 = [1,2, ...arr]; console.log(arr2);//[1 2 3 4 5] console.log(...arr1);//1 2 3 4 5
const arr = [3,4,5];
const arr1 = [1,2,arr[0],arr[1],arr[2]];
const arr2 = [1,2, ...arr];
console.log(arr2);//[1 2 3 4 5]
console.log(...arr1);//1 2 3 4 5- Iterables: arrays, strings, maps, set, BUT NOT objects
- Although objects are not iterable, the spread operater works on objects
const str = 'hello';
const letters = [...str,'',...'world'];
console.log(letters);
const workdays = {Mon:1,Tue:2,Wed:3,Thu:4,Fri:5};
const weekdays = {...workdays,Sat:6,Sun:7};
console.log(weekdays.Sat);//output:6const str = 'hello';
const letters = [...str,'',...'world'];
console.log(letters);
const workdays = {Mon:1,Tue:2,Wed:3,Thu:4,Fri:5};
const weekdays = {...workdays,Sat:6,Sun:7};
console.log(weekdays.Sat);//output:6Rest pattern and parameters
- Object
const arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6];
const [x,/*y*/,z,...arr2] = [1,2,...arr1]; // the rest pattern has to be at the last position on the left of assignment operation;
console.log(x,z,arr2);//x=1,z=1,arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6]
const weekdays = {Mon:1,Tue:2,Wed:3,Thu:4,Fri:5,Sat:6,Sun:7};
const {Sat,Sun,...workdays} = weekdays;
console.log(workdays);// {Mon: 1, Tue: 2, Wed: 3, Thu: 4, Fri: 5}const arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6];
const [x,/*y*/,z,...arr2] = [1,2,...arr1]; // the rest pattern has to be at the last position on the left of assignment operation;
console.log(x,z,arr2);//x=1,z=1,arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6]
const weekdays = {Mon:1,Tue:2,Wed:3,Thu:4,Fri:5,Sat:6,Sun:7};
const {Sat,Sun,...workdays} = weekdays;
console.log(workdays);// {Mon: 1, Tue: 2, Wed: 3, Thu: 4, Fri: 5}- Function(rest parameters)
function add(...numbers){
console.log(numbers);//numbers = [1, 2, 3]
let sum = 0;
for (let index = 0; index < numbers.length; index++) {
sum += numbers[index];
}
console.log(sum);
}
add(1,2,3);//output 6
const x = [1,2,3];
add(...x);//output 6function add(...numbers){
console.log(numbers);//numbers = [1, 2, 3]
let sum = 0;
for (let index = 0; index < numbers.length; index++) {
sum += numbers[index];
}
console.log(sum);
}
add(1,2,3);//output 6
const x = [1,2,3];
add(...x);//output 6Short circuiting(||,&&)
-
Can use ANY data type, return ANY data type, short-circuiting
-
OR operation:
short-circuiting: it will immediately return the first truthy value, or the last falsy value when there are no truthy value at all.
console.log(3||'hello');//output:3
console.log(3||'hello');//output:3 - AND operation:
short-circuiting: it will immediately return the first falsy value, or the last truthy value when there are no falsy value after checking every element.
console.log(0&&3);//output:0
console.log(0&&3);//output:0Nullish Coalescing Operator (??)
- Nullish value: null and undefined
let x; const y = 3; console.log(x??y);//output 3 x = 0; console.log(x??y);//output 0, because 0 is not nullish console.log(x||y);//output 3, because 0 is a falsy value
let x;
const y = 3;
console.log(x??y);//output 3
x = 0;
console.log(x??y);//output 0, because 0 is not nullish
console.log(x||y);//output 3, because 0 is a falsy valueOR,AND,Nullish assignment operator
let x = 0; x ||= 10;//x = x||10; console.log(x);//output:10, because 0 is falsy x = 0; x &&= 10;// x = x&&10; console.log(x);//output:0 x ??= 10; console.log(x);//output:0,because x=0 is not nullish
let x = 0;
x ||= 10;//x = x||10;
console.log(x);//output:10, because 0 is falsy
x = 0;
x &&= 10;// x = x&&10;
console.log(x);//output:0
x ??= 10;
console.log(x);//output:0,because x=0 is not nullishFor-of loop
const days = ['mon','tue','wed','thu','fri','sat','sun'];
for (const day of days) {
console.log(day);
}
for (const day of days.entries()) {
console.log(day);
}
/* Array Iterator
Output:
(2) [0, 'mon']
(2) [1, 'tue']
(2) [2, 'wed']
(2) [3, 'thu']
(2) [4, 'fri']
(2) [5, 'sat']
(2) [6, 'sun'] */const days = ['mon','tue','wed','thu','fri','sat','sun'];
for (const day of days) {
console.log(day);
}
for (const day of days.entries()) {
console.log(day);
}
/* Array Iterator
Output:
(2) [0, 'mon']
(2) [1, 'tue']
(2) [2, 'wed']
(2) [3, 'thu']
(2) [4, 'fri']
(2) [5, 'sat']
(2) [6, 'sun'] */Object Literals
Optional Chaining(?.)
const hours ={Mon:{open:'8-17'},Tue:'8-17',Wed:'8-17',Thu:'8-17',Fri:{open:{normal:{holidays:'not open',workdays:'8-20'}}}};
console.log(hours.Mon?.open);//Will return correct value
console.log(hours.Tue.open);//Will return undefined
console.log(hours.Sat?.open);//Will return undefined
console.log(hours.Sat.open);//Error will occur(TypeError: Cannot read property 'open' of undefined) since object 'Sat' is undefined, undefined datatype can't have property.
console.log(hours.Fri.open.normal.workdays);//Will return correct value
console.log(hours.Thu.open?.normal.workdays);//Will return undefined, because there is an object called 'Thu' while 'normal' is undefined.
console.log(hours.Thu.open.normal?.workdays);//Error will occur(TypeError: Cannot read property 'normal' of undefined) since object 'Open' is undefined, undefined datatype can't have property.const hours ={Mon:{open:'8-17'},Tue:'8-17',Wed:'8-17',Thu:'8-17',Fri:{open:{normal:{holidays:'not open',workdays:'8-20'}}}};
console.log(hours.Mon?.open);//Will return correct value
console.log(hours.Tue.open);//Will return undefined
console.log(hours.Sat?.open);//Will return undefined
console.log(hours.Sat.open);//Error will occur(TypeError: Cannot read property 'open' of undefined) since object 'Sat' is undefined, undefined datatype can't have property.
console.log(hours.Fri.open.normal.workdays);//Will return correct value
console.log(hours.Thu.open?.normal.workdays);//Will return undefined, because there is an object called 'Thu' while 'normal' is undefined.
console.log(hours.Thu.open.normal?.workdays);//Error will occur(TypeError: Cannot read property 'normal' of undefined) since object 'Open' is undefined, undefined datatype can't have property.Looping objects
const hours = {Monday:{open:'8',close:'17'},Tuesday:{open:'8',close:'17'},Wednesday:{open:'8',close:'17'},Thursday:{open:'8',close:'20'},Friday:{open:'8',close:'21'}};
for (const day of Object.keys(hours)) {
console.log(day); // Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri
}
const days = Object.keys(hours);
const openHours = Object.values(hours);
console.log(days);//['Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri'] array
console.log(openHours);//array of values
for (const [day,{open,close}] of Object.entries(hours)) {
console.log(`${day} open at ${open}, close at ${close}`); //Monday open at 8, close at 17 Tuesday open at 8, close at 17 ...
}const hours = {Monday:{open:'8',close:'17'},Tuesday:{open:'8',close:'17'},Wednesday:{open:'8',close:'17'},Thursday:{open:'8',close:'20'},Friday:{open:'8',close:'21'}};
for (const day of Object.keys(hours)) {
console.log(day); // Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri
}
const days = Object.keys(hours);
const openHours = Object.values(hours);
console.log(days);//['Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri'] array
console.log(openHours);//array of values
for (const [day,{open,close}] of Object.entries(hours)) {
console.log(`${day} open at ${open}, close at ${close}`); //Monday open at 8, close at 17 Tuesday open at 8, close at 17 ...
}Object Methods
Object.freeze()//Can not add new entry into Object, but still be able to edit the entry
Object.freeze()//Can not add new entry into Object, but still be able to edit the entrySet
- Iterable
.size
.has()
.add()
.delete()
.clear() //delete all the elements in a set
const numbers = [1,2,3,1,2,4,5,6];
const set = new Set(numbers);
console.log(set);// {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
console.log(new Set('12312').size);//3
//forEach
const set2 = new Set(['USD','GBP','USD','EUR']);
set2.forEach(function(value,_,set){
console.log(`${value}:${_}`);
});
/*
USD:USD
map.js:18
GBP:GBP
map.js:18
EUR:EUR
*/.size
.has()
.add()
.delete()
.clear() //delete all the elements in a set
const numbers = [1,2,3,1,2,4,5,6];
const set = new Set(numbers);
console.log(set);// {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
console.log(new Set('12312').size);//3
//forEach
const set2 = new Set(['USD','GBP','USD','EUR']);
set2.forEach(function(value,_,set){
console.log(`${value}:${_}`);
});
/*
USD:USD
map.js:18
GBP:GBP
map.js:18
EUR:EUR
*/Map
.size
.set()
.get()
.has()
.delete()
.claer()
const map = new Map();
console.log(map.set(1,'One'));//Map(1) {1 => One}
map.set('Tow',2).set(true,'1+2=3');
console.log(map.get(true));//1+2=3const map = new Map();
console.log(map.set(1,'One'));//Map(1) {1 => One}
map.set('Tow',2).set(true,'1+2=3');
console.log(map.get(true));//1+2=3- Map Iterator:
const map = new Map();
map.keys() //data type:Map Iterator
map.values() //data type:Map Iterator
map.entries() //data type:Map Iterator
//forEach:
const currencies = new Map([['USD','United States Dollar'],['EUR','Euro'],['GBP','Pound']]);
currencies.forEach(function(value,key,map){
console.log(`${key} : 1 ${value}`);
});
/*
USD : 1 United States Dollar
EUR : 1 Euro
GBP : 1 Pound*/const map = new Map();
map.keys() //data type:Map Iterator
map.values() //data type:Map Iterator
map.entries() //data type:Map Iterator
//forEach:
const currencies = new Map([['USD','United States Dollar'],['EUR','Euro'],['GBP','Pound']]);
currencies.forEach(function(value,key,map){
console.log(`${key} : 1 ${value}`);
});
/*
USD : 1 United States Dollar
EUR : 1 Euro
GBP : 1 Pound*/const question = new Map(
[
['question','The best language is? '],
[1,'C'],
[2,'Java'],
[3,'JavaSctipt'],
['correct',3],
[true,'You are correct!'],
[false,'Try again!']
]
);
console.log(question.get('question'));
for (const [key,value] of Object.entries(question)) {
}
const answer = Number(prompt('Your answer'));
question.get('correct') === answer ? console.log(question.get(true)) : console.log(question.get(false));
const arr = [...question] //convert map to arrayconst question = new Map(
[
['question','The best language is? '],
[1,'C'],
[2,'Java'],
[3,'JavaSctipt'],
['correct',3],
[true,'You are correct!'],
[false,'Try again!']
]
);
console.log(question.get('question'));
for (const [key,value] of Object.entries(question)) {
}
const answer = Number(prompt('Your answer'));
question.get('correct') === answer ? console.log(question.get(true)) : console.log(question.get(false));
const arr = [...question] //convert map to arrayString
const airline = 'Air France';
console.log(airline.indexOf('i')); // 1
console.log(airline.indexOf('d')); //-1
console.log(airline.indexOf('r')); //2
console.log(airline.lastIndexOf('r')); //5
console.log(airline.length); //10
console.log(airline.slice(4)); //output: France
console.log(airline.slice(4,5)); //output: F
console.log(airline.slice(-6)); //output: France
console.log(airline.slice(0,airline.indexOf(' '))); //output: Air
console.log(airline.charAt(airline.length-1));//e
console.log(airline[airline.length-1]);//e
console.log(airline.at(-1));//e
const airlineLower = airline.toLowerCase();
const airlineCorrect = airline[0].toUpperCase()+airline.slice(1,4)+airline[4].toUpperCase()+airline.slice(5);
console.log(airlineLower);//air france
console.log(airlineCorrect);//Air France
//.trim()
const email = 'rua9@pitt.edu';
const typedEmail = ' RUA9@Pitt.edu \n';
const trimmedLowerEmail = typedEmail.toLowerCase().trim();
console.log(trimmedLowerEmail);//rua9@pitt.edu
const annoucement = 'Hello World, Hello you!';
console.log(annoucement.replace('Hello','Hi'));//output: Hi World, Hello you!
console.log(annoucement.replace(/Hello/g,'Hi'));//output: Hi World, Hi you! Regular Expression replaced all 'Hello'
console.log(annoucement.includes('hello'));//false
console.log(annoucement.includes('Hello'));//true
console.log(annoucement.startsWith('He'));//true
console.log(annoucement.endsWith('ou!'));//true
//split & join
console.log(annoucement.split('o'));//['Hell', ' W', 'rld, Hell', ' y', 'u!']
const [str1,str2] = annoucement.split(',');
console.log(str1,str2);//Hello World Hello you!
const newAnnouncement = ['Hello', str1.toLowerCase(), str2.toLowerCase()].join(' ');//Hello hello world hello you!
console.log(newAnnouncement);
//padding to a particular length
const message = '12345';
console.log(message.padStart(10,'+'));
console.log(message.padEnd(10,'+'));
//repeat
console.log(message.repeat(3));
const airline = 'Air France';
console.log(airline.indexOf('i')); // 1
console.log(airline.indexOf('d')); //-1
console.log(airline.indexOf('r')); //2
console.log(airline.lastIndexOf('r')); //5
console.log(airline.length); //10
console.log(airline.slice(4)); //output: France
console.log(airline.slice(4,5)); //output: F
console.log(airline.slice(-6)); //output: France
console.log(airline.slice(0,airline.indexOf(' '))); //output: Air
console.log(airline.charAt(airline.length-1));//e
console.log(airline[airline.length-1]);//e
console.log(airline.at(-1));//e
const airlineLower = airline.toLowerCase();
const airlineCorrect = airline[0].toUpperCase()+airline.slice(1,4)+airline[4].toUpperCase()+airline.slice(5);
console.log(airlineLower);//air france
console.log(airlineCorrect);//Air France
//.trim()
const email = 'rua9@pitt.edu';
const typedEmail = ' RUA9@Pitt.edu \n';
const trimmedLowerEmail = typedEmail.toLowerCase().trim();
console.log(trimmedLowerEmail);//rua9@pitt.edu
const annoucement = 'Hello World, Hello you!';
console.log(annoucement.replace('Hello','Hi'));//output: Hi World, Hello you!
console.log(annoucement.replace(/Hello/g,'Hi'));//output: Hi World, Hi you! Regular Expression replaced all 'Hello'
console.log(annoucement.includes('hello'));//false
console.log(annoucement.includes('Hello'));//true
console.log(annoucement.startsWith('He'));//true
console.log(annoucement.endsWith('ou!'));//true
//split & join
console.log(annoucement.split('o'));//['Hell', ' W', 'rld, Hell', ' y', 'u!']
const [str1,str2] = annoucement.split(',');
console.log(str1,str2);//Hello World Hello you!
const newAnnouncement = ['Hello', str1.toLowerCase(), str2.toLowerCase()].join(' ');//Hello hello world hello you!
console.log(newAnnouncement);
//padding to a particular length
const message = '12345';
console.log(message.padStart(10,'+'));
console.log(message.padEnd(10,'+'));
//repeat
console.log(message.repeat(3));
Functions
Call and Apply method:
- Use .call() or .apply() when you want to invoke the function immediately, and modify the context.
const uberOrder = {
restaurant: 'KFC',
food: 'fried chicken',
order(number,addr){
console.log(`${number} * ${this.food} to ${addr}`);
}
};
const makeOrder = uberOrder.order;
//call method:
makeOrder.call(uberOrder,5,'university of pittsburgh');//5 * fried chiecken, The call() method calls the function with a given this value and arguments provided individually.
makeOrder(3);//error, this not defined
//apply method:
makeOrder.apply(uberOrder,[3,'apt305']);//The apply() method calls the specified function with a given "this" value, and arguments provided as an array (or an array-like object)
const uberOrder = {
restaurant: 'KFC',
food: 'fried chicken',
order(number,addr){
console.log(`${number} * ${this.food} to ${addr}`);
}
};
const makeOrder = uberOrder.order;
//call method:
makeOrder.call(uberOrder,5,'university of pittsburgh');//5 * fried chiecken, The call() method calls the function with a given this value and arguments provided individually.
makeOrder(3);//error, this not defined
//apply method:
makeOrder.apply(uberOrder,[3,'apt305']);//The apply() method calls the specified function with a given "this" value, and arguments provided as an array (or an array-like object)
Bind method
- Use .bind() when you want that function to later be called with a certain context, useful in events.
const orderBind = makeOrder.bind(uberOrder);
orderBind(10,'PITT'); //output: 10 * fried chicken to PITT (this keyword has been bound to the uberOrder object)
const orderBind7 = makeOrder.bind(uberOrder,7);
orderBind7('my apartment');//output: 7 * fried chicken to my apartment
//using with DOM
document.querySelector('.buy').addEventListener('click',uberOrder.buyPlane);//output: undefined has bought a new plane for delivery; Reason: 'this' keyword point to the button;
document.querySelector('.buy').addEventListener('click',uberOrder.buyPlane.bind(uberOrder));//output: KFC has bought a new plane for delivery
//partially bind
const tax = (rate,value) => value+rate*value;
console.log(tax(0.1,200));//220
const fixedTax = tax.bind(null,0.2);
console.log(fixedTax(200));//240
//same result using return function
const tax2 = function(rate){
return function(value){
return value+value*rate;
}
};
const fixedTax2 = tax2(0.2);
console.log(fixedTax2(200));//240const orderBind = makeOrder.bind(uberOrder);
orderBind(10,'PITT'); //output: 10 * fried chicken to PITT (this keyword has been bound to the uberOrder object)
const orderBind7 = makeOrder.bind(uberOrder,7);
orderBind7('my apartment');//output: 7 * fried chicken to my apartment
//using with DOM
document.querySelector('.buy').addEventListener('click',uberOrder.buyPlane);//output: undefined has bought a new plane for delivery; Reason: 'this' keyword point to the button;
document.querySelector('.buy').addEventListener('click',uberOrder.buyPlane.bind(uberOrder));//output: KFC has bought a new plane for delivery
//partially bind
const tax = (rate,value) => value+rate*value;
console.log(tax(0.1,200));//220
const fixedTax = tax.bind(null,0.2);
console.log(fixedTax(200));//240
//same result using return function
const tax2 = function(rate){
return function(value){
return value+value*rate;
}
};
const fixedTax2 = tax2(0.2);
console.log(fixedTax2(200));//240Immediately Invoked Function Expression(IIFE)
(function(){
console.log('only run once');
})();
(()=>console.log('This will only run once as well'))();(function(){
console.log('only run once');
})();
(()=>console.log('This will only run once as well'))();Closures
- A closure is a function having access to the parent scope, even after the parent function has closed.
const add = (function () {
let counter = 0;
return function () {counter += 1; return counter}
})();
console.log(typeof(add));//function
add();//1
add();//2
add();//3const add = (function () {
let counter = 0;
return function () {counter += 1; return counter}
})();
console.log(typeof(add));//function
add();//1
add();//2
add();//3Array2
Array Methods
//Slice
let arr = ['a','b','c','d','e'];
console.log(arr.slice(2));//['c', 'd', 'e']
console.log(arr);//['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] array doesn't change
//Splice
//The splice() method changes the contents of an array by removing or replacing existing elements and/or adding new elements in place.
//To create a new array with a segment removed and/or replaced without mutating the original array, use toSpliced(). To access part of an array without modifying it, see slice().
console.log(arr.splice(2));//['c', 'd', 'e']
console.log(arr);//['a', 'b'] original array has been mutated
//Parameter: splice(startIndex, deleteCount, item0, item1)
//reverse
const arr2 = ['j','i','h','g','f'];
console.log(arr2.reverse());//['f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j']
console.log(arr2);//['f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j'] original array changed as well
//concat
arr = ['a','b','c','d','e'];
const letters = arr.concat(arr2);
console.log(letters);// ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j']
console.log(arr);// ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
//join
console.log(letters.join('-')); // a-b-c-d-e-f-g-h-i-j
console.log(letters);// ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j']
//at
console.log(arr[arr.length-1]);//e
console.log(arr.at(-1));//e
console.log(arr[-1]);//undefined
//every
const ages = [32, 33, 16, 40];
const ages2 = [32, 33, 20, 40];
const agesOlderThan18 = ages.every((age) => age > 18);
const ages2OlderThan18 = ages2.every((age) => age > 18);
console.log(agesOlderThan18); //false
console.log(ages2OlderThan18); //true
//some
//The some() method tests whether at least one element in the array passes the test implemented by the provided function.
//It returns true if, in the array, it finds an element for which the provided function returns true;
//otherwise it returns false. It doesn't modify the array.
const someArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const even = (element) => element % 2 === 0; //Function to check whether an element is even
console.log(someArray.some(even)); //true
//find
//The find() method returns the first element in the provided array that satisfies the provided testing function.
//If no values satisfy the testing function, undefined is returned.
const findArray = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const found = findArray.find((element) => element > 10);
console.log(found); //12
//findIndex
//The findIndex() method returns the index of the first element in an array that satisfies the provided testing function.
//If no elements satisfy the testing function, -1 is returned.
const findIndexArr = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const isLarger = (element) => element > 10;
console.log(findIndexArr.findIndex(isLarger)); //1
//Slice
let arr = ['a','b','c','d','e'];
console.log(arr.slice(2));//['c', 'd', 'e']
console.log(arr);//['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] array doesn't change
//Splice
//The splice() method changes the contents of an array by removing or replacing existing elements and/or adding new elements in place.
//To create a new array with a segment removed and/or replaced without mutating the original array, use toSpliced(). To access part of an array without modifying it, see slice().
console.log(arr.splice(2));//['c', 'd', 'e']
console.log(arr);//['a', 'b'] original array has been mutated
//Parameter: splice(startIndex, deleteCount, item0, item1)
//reverse
const arr2 = ['j','i','h','g','f'];
console.log(arr2.reverse());//['f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j']
console.log(arr2);//['f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j'] original array changed as well
//concat
arr = ['a','b','c','d','e'];
const letters = arr.concat(arr2);
console.log(letters);// ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j']
console.log(arr);// ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
//join
console.log(letters.join('-')); // a-b-c-d-e-f-g-h-i-j
console.log(letters);// ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j']
//at
console.log(arr[arr.length-1]);//e
console.log(arr.at(-1));//e
console.log(arr[-1]);//undefined
//every
const ages = [32, 33, 16, 40];
const ages2 = [32, 33, 20, 40];
const agesOlderThan18 = ages.every((age) => age > 18);
const ages2OlderThan18 = ages2.every((age) => age > 18);
console.log(agesOlderThan18); //false
console.log(ages2OlderThan18); //true
//some
//The some() method tests whether at least one element in the array passes the test implemented by the provided function.
//It returns true if, in the array, it finds an element for which the provided function returns true;
//otherwise it returns false. It doesn't modify the array.
const someArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const even = (element) => element % 2 === 0; //Function to check whether an element is even
console.log(someArray.some(even)); //true
//find
//The find() method returns the first element in the provided array that satisfies the provided testing function.
//If no values satisfy the testing function, undefined is returned.
const findArray = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const found = findArray.find((element) => element > 10);
console.log(found); //12
//findIndex
//The findIndex() method returns the index of the first element in an array that satisfies the provided testing function.
//If no elements satisfy the testing function, -1 is returned.
const findIndexArr = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const isLarger = (element) => element > 10;
console.log(findIndexArr.findIndex(isLarger)); //1
foreach loop
- break and continue doesn't work for each loop
const movements = [200,450,-100,300,-400,800,-50,140];
movements.forEach(function(movement){
movement>0? console.log(`You deposit ${movement} bucks`) : console.log(`You withdraw ${Math.abs(movement)} bucks`);
});
movements.forEach(function(movement,index,array){
movement>0? console.log(`Movement${index+1} : You deposit ${movement} bucks`) : console.log(`Movement${index+1} :You withdraw ${Math.abs(movement)} bucks`);
console.log(array);//[200, 450, -100, 300, -400, 800, -50, 140]
});const movements = [200,450,-100,300,-400,800,-50,140];
movements.forEach(function(movement){
movement>0? console.log(`You deposit ${movement} bucks`) : console.log(`You withdraw ${Math.abs(movement)} bucks`);
});
movements.forEach(function(movement,index,array){
movement>0? console.log(`Movement${index+1} : You deposit ${movement} bucks`) : console.log(`Movement${index+1} :You withdraw ${Math.abs(movement)} bucks`);
console.log(array);//[200, 450, -100, 300, -400, 800, -50, 140]
});Array.map() method
const eurToUsd = 1.1;
const movementsUsd = movements.map(function(move){
return move*eurToUsd;
});
console.log(movements);//[200, 450, -100, 300, -400, 800, -50, 140] map function doesn't mutate original array;
console.log(movementsUsd);//[220.00000000000003, 495.00000000000006, -110.00000000000001, 330, -440.00000000000006, 880.0000000000001, -55.00000000000001, 154] map function returns a new array;const eurToUsd = 1.1;
const movementsUsd = movements.map(function(move){
return move*eurToUsd;
});
console.log(movements);//[200, 450, -100, 300, -400, 800, -50, 140] map function doesn't mutate original array;
console.log(movementsUsd);//[220.00000000000003, 495.00000000000006, -110.00000000000001, 330, -440.00000000000006, 880.0000000000001, -55.00000000000001, 154] map function returns a new array;Filter
const deposits = movements.filter(function(move){
return move>0;
});
console.log(deposits);//[200, 450, 300, 800, 140]
console.log(movements);//[200, 450, -100, 300, -400, 800, -50, 140] filter method doen't mutate the original array.const deposits = movements.filter(function(move){
return move>0;
});
console.log(deposits);//[200, 450, 300, 800, 140]
console.log(movements);//[200, 450, -100, 300, -400, 800, -50, 140] filter method doen't mutate the original array.reduce and reduceRight
const myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const callbackfn = (sum, element) => (sum += element); let initialValue = 1; console.log(myArray.reduce(callbackfn)); //10 console.log(myArray.reduce(callbackfn, initialValue)); //11 const myString = ["hello", " world", " !"]; const callbackfn2 = (str, subStr) => (str += subStr); console.log(myString.reduce(callbackfn2)); //hello world ! //The reduceRight() method applies a function against an accumulator and each value of the array (from right-to-left) to reduce it to a single value. console.log(myString.reduceRight(callbackfn2)); // ! worldhello const initialValue2 = "Say "; console.log(myString.reduce(callbackfn2, initialValue2)); //Say hello world ! console.log(myString.reduceRight(callbackfn2, initialValue2)); //Say ! worldhello
const myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const callbackfn = (sum, element) => (sum += element);
let initialValue = 1;
console.log(myArray.reduce(callbackfn)); //10
console.log(myArray.reduce(callbackfn, initialValue)); //11
const myString = ["hello", " world", " !"];
const callbackfn2 = (str, subStr) => (str += subStr);
console.log(myString.reduce(callbackfn2)); //hello world !
//The reduceRight() method applies a function against an accumulator and each value of the array (from right-to-left) to reduce it to a single value.
console.log(myString.reduceRight(callbackfn2)); // ! worldhello
const initialValue2 = "Say ";
console.log(myString.reduce(callbackfn2, initialValue2)); //Say hello world !
console.log(myString.reduceRight(callbackfn2, initialValue2)); //Say ! worldhello//Sorting array of Ints //Principle: use a function to compare a and b, if the function returns an INT>0, a will be placed after b. //if it returns a negative INT, a will be placed before b. const arr1 = [3, 7, 1, 9, 6]; const sorted1 = arr1.sort((a, b) => a - b); //Ascending sequence, if a-b returns a positive value(a>b), a will be placed after b and vice versa. console.log(sorted1); //[1, 3, 6, 7, 9] console.log(arr1); //[9, 7, 6, 3, 1] The sort method mutate the original array. const sorted2 = arr1.slice().sort((a, b) => b - a); //Descending sequence, if b-a returns a positive value(b>a), a will be placed after b and vice versa. console.log(sorted2); //[9, 7, 6, 3, 1] console.log(arr1); //[1, 3, 6, 7, 9] // By using .slice() to create a new array,the original array wasn't mutated //Sorting array of objects based on its String property array.sort((element1,element2)=>element1.name.localeCompare(element2.name)) //localeCompare() is a String method wich returns a negative INT if String1<String2
//Sorting array of Ints
//Principle: use a function to compare a and b, if the function returns an INT>0, a will be placed after b.
//if it returns a negative INT, a will be placed before b.
const arr1 = [3, 7, 1, 9, 6];
const sorted1 = arr1.sort((a, b) => a - b); //Ascending sequence, if a-b returns a positive value(a>b), a will be placed after b and vice versa.
console.log(sorted1); //[1, 3, 6, 7, 9]
console.log(arr1); //[9, 7, 6, 3, 1] The sort method mutate the original array.
const sorted2 = arr1.slice().sort((a, b) => b - a); //Descending sequence, if b-a returns a positive value(b>a), a will be placed after b and vice versa.
console.log(sorted2); //[9, 7, 6, 3, 1]
console.log(arr1); //[1, 3, 6, 7, 9] // By using .slice() to create a new array,the original array wasn't mutated
//Sorting array of objects based on its String property
array.sort((element1,element2)=>element1.name.localeCompare(element2.name))
//localeCompare() is a String method wich returns a negative INT if String1<String2Array methods
| will mutate original array | will create a new array | to get index of an element | to know if array includes | to transform to value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Add to original: .push(end of array) .unshift(start of array) | Computed from original array: .map | To get the index of a value: .indexOf(Based on value) .findIndex(Based on test condition) | Based on value of element: .includes | Based on accumulator: .reduce |
| Remove from original: .pop(element at the end, last index) .shift(element at the start, first index) .splice(depends on the index parameters) | Filtered using condition: .filter | Based on test condition: .some .every | ||
| Others: .reverse .sort .fill | Portion of original: .slice | to get an element in array | to just loop array | |
| Adding original array to other: .concat | .find(Based on test condition) | to create a new String: | Based on callback: .foreach(Does not create a new array, just loops over the original) | |
| Flattening the original: .flat .flatMap | .join(Based on separator String) |
DOM and Events
Script Loading
- Regular(put the script tag at the end of body in HTML)
- Async in Head:
Scripts are fetched asynchronously and executed immediately - Defer in Head:
Scripts are fetched asynchronously and executed after the HTML is completely parsed
<head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" /> <script async src="async_script.js"></script> <script defer src="defer_script.js"></script> </head>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<script async src="async_script.js"></script>
<script defer src="defer_script.js"></script>
</head>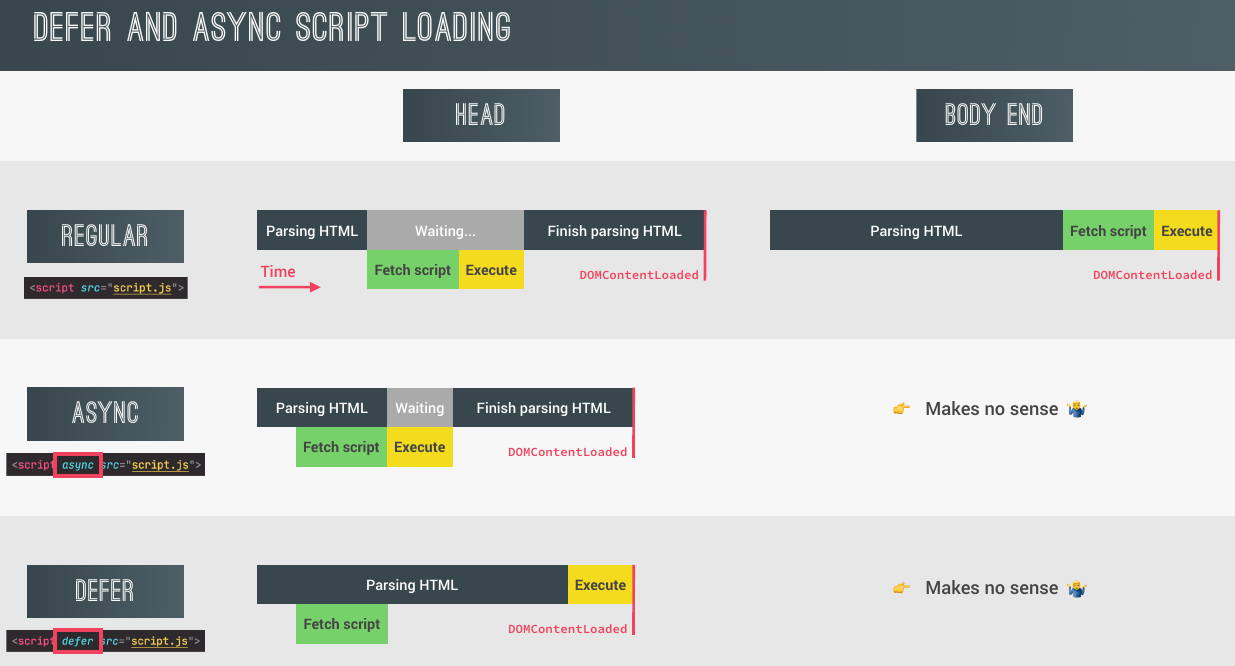

DOM contents
Element: closest() method
- The closest() method of the Element interface traverses the element and its parents (heading toward the document root) until it finds a node that matches the specified CSS selector.
//Find out the closest element to the e.target
parentElement.addEventListener("click", function (e) {
const button = e.target.closest(".btn--inline");
if (!button) return;
const gotoPage = +button.dataset.goto;
handler(gotoPage);
});
//Find out the closest element to the e.target
parentElement.addEventListener("click", function (e) {
const button = e.target.closest(".btn--inline");
if (!button) return;
const gotoPage = +button.dataset.goto;
handler(gotoPage);
});
Dataset Property
- The dataset read-only property of the HTMLElement interface provides read/write access to custom data attributes (data-) on elements. It exposes a map of strings (DOMStringMap) with an entry for each data- attribute.
<button data-goto="1" class="btn--inline">Goto Page</button>
<button data-goto="1" class="btn--inline">Goto Page</button> const button = document.querySelector(".btn--inline");
const gotoPage = +button.dataset.goto;//Convert String to numberconst button = document.querySelector(".btn--inline");
const gotoPage = +button.dataset.goto;//Convert String to numberAppendChild
InsertAdjacentHTML
InnerHTML vs
<body>
<div id="div1">
This element is
<h1>Headline</h1>
<em>and this is some emphasized text.</em>
</div>
<script>
const content = document.getElementById("div1");
console.log(content.innerHTML);
//This element is "<h1>Headline</h1> <em>and this is some emphasized text.</em>"
console.log(content.innerText);
/*This element is "Headline and this is some emphasized text."*/
console.log(content.textContent);
/*This element is Headline and this is some emphasized text.*/
</script>
</body><body>
<div id="div1">
This element is
<h1>Headline</h1>
<em>and this is some emphasized text.</em>
</div>
<script>
const content = document.getElementById("div1");
console.log(content.innerHTML);
//This element is "<h1>Headline</h1> <em>and this is some emphasized text.</em>"
console.log(content.innerText);
/*This element is "Headline and this is some emphasized text."*/
console.log(content.textContent);
/*This element is Headline and this is some emphasized text.*/
</script>
</body>- innerText was non-standard, textContent was standardized earlier.
- innerText returns the visible text contained in a node, while textContent returns the full text. For example, on the following HTML
<span>Hello <span style="display: none;">World</span></span>
innerText will return 'Hello', while textContent will return 'Hello World'.
For a more complete list of differences, see the table at http://perfectionkills.com/the-poor-misunderstood-innerText/ (further reading at 'innerText' works in IE, but not in Firefox). - As a result, innerText is much more performance-heavy: it requires layout information to return the result.
- innerText is defined only for HTMLElement objects, while textContent is defined for all Node objects.
Object Oriented Programming
4 Foundamental Principles(4 pillars)
- Abstraction: Ignoring or hiding details that don't matter, avoid messing with details that don't really matter our implementation
- Encapsulation: Keep properties and methods private inside the class, So they are not accessible from outside the class. Some methods can be exposed as a public interface(API blackbox).
- Inheritance: Making all properties and methods of a certain class available to a child class, forming a hierarchical relationship between classes. This allows us to reuse common logic and to model real-world relationships.
- Polymorphism: A child class can overwrite a method it inherited from a parent class.
OOP in JavaScript
In Classical OOP
Objects(instances) are instantiated from a Class, which functions like a blueprint
OOP in JS: Prototypes
- Objects are linked to a prototype object
- Prototypal inheritance: The prototype contains methods(behaviour) that are accessible to all objects linked to that prototype.
- Behavior is delegated to the linked prototype object.
3 ways to implement Prototypal Inheritance in JavaScript
- Constructor functions:
- Technique to create objects from a function
- This is how built-in objects like Arrays,Maps or Sets are actually implemented
- ES6 Classes
- Modern alternative to constructor function syntax
- "Syntactic sugar": behind the scenes, ES6 classes work exactly like constructor functions
- ES6 classes do not behave like classes in "classical OOP"
- Object.create()
- The easist and most straightforward way of linking an object to a prototype object
Asynchronous
Synchronous vs Asynchronous
Line by line vs Runs in the "background"
Blocking the afterwards code execution vs Non blocking
- Asynchronous example:
- setTimeout
const timeoutID = setTimeout(function(){
console.log("Hello World!")
},5000)//5000 = 5 seconds
clearTimeout(timeoutID); // Remove the timeoutconst timeoutID = setTimeout(function(){
console.log("Hello World!")
},5000)//5000 = 5 seconds
clearTimeout(timeoutID); // Remove the timeout- Set .src attribute and .addEventListener
const img = document.querySelector('.pic');//Sync
img.src='doc.jpg';//Async (Loading in background)
//The handler itself is Async, waiting for the finish of loading (while addEventListener is Sync)
img.addEventListener('load',function(){
img.classList.add('fadeIn');
});
p.style.width = '300px'; //Sync, execution not blocked by the 2 Async codeconst img = document.querySelector('.pic');//Sync
img.src='doc.jpg';//Async (Loading in background)
//The handler itself is Async, waiting for the finish of loading (while addEventListener is Sync)
img.addEventListener('load',function(){
img.classList.add('fadeIn');
});
p.style.width = '300px'; //Sync, execution not blocked by the 2 Async code- setInterval
const intervalID = setInterval(function(){
console.log("Hello World!")
},500)//Call the function every 0.5 second
clearInterval(intervalID) // Remove the interval const intervalID = setInterval(function(){
console.log("Hello World!")
},500)//Call the function every 0.5 second
clearInterval(intervalID) // Remove the intervalAJAX
- Asynchronous JavaScript And XML:
Communicate with remote web servers in an Asynchronous way. With AJAX, can request data from web servers dynamically.(without reload page).
XML is not used anymore, replaced by JSON
API
- Application Programming Interface:
Can be used by another piece of code/software, in order to allow applications talking with each other - Examples:
DOM API
Geolocation API
Own Class API
Web API("Online" API)
- Application running on a remote server, receives request for data, and sends data back as response.
Leaflet map
localStorage
- Can check in the browser's dev tool -> Application -> Local Storage
const dataToSave = "aString" || JSON.stringfy(object)
localStorage.setItem('dataIdentifier',dataToSave)
const data = localStorage.getItem('dataIdentifier')
localStorage.clear('dataIdentifier')const dataToSave = "aString" || JSON.stringfy(object)
localStorage.setItem('dataIdentifier',dataToSave)
const data = localStorage.getItem('dataIdentifier')
localStorage.clear('dataIdentifier')JSON
JSON.stringify() JSON.parse()
JSON.stringify()
JSON.parse()Promise
- An object that is used as a placeholder for the future result of an asynchronous operation.
(A container for a future value )
Promise Lifecycle
Consume Promise
Chaining Promise
- .then() method always return a promise
- If the Promise is fufilled, the successful value will be returned
- .finally()
Error
- .then().catch()
fetch(url)
.then((response) => {
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("This is the error"); //Will terminate .then() handler and error will be catched by the .catch() method
}
return response.json();
})
.then(function (json) {
const [data] = json;
return data
})
.catch((err) => {
//Catch all the error in the .then() chain, it also returns a promise
//renderError(`Something went wrong - ${err.message}. Try again!`); //If no specified error threw previously, the error essage will be Something went wrong - json is not iterable. Try again!
console.error(err.message); //Log the thrown error.message from previous steps
})
.finally(
//always happen no matter the result of the promise
(countriesContainer.style.opacity = 1)
);fetch(url)
.then((response) => {
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("This is the error"); //Will terminate .then() handler and error will be catched by the .catch() method
}
return response.json();
})
.then(function (json) {
const [data] = json;
return data
})
.catch((err) => {
//Catch all the error in the .then() chain, it also returns a promise
//renderError(`Something went wrong - ${err.message}. Try again!`); //If no specified error threw previously, the error essage will be Something went wrong - json is not iterable. Try again!
console.error(err.message); //Log the thrown error.message from previous steps
})
.finally(
//always happen no matter the result of the promise
(countriesContainer.style.opacity = 1)
);- Try-Catch
try {
let y = 1;
const x = 2;
x = 3;
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.message);
}try {
let y = 1;
const x = 2;
x = 3;
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.message);
}Promisify
Event Loop
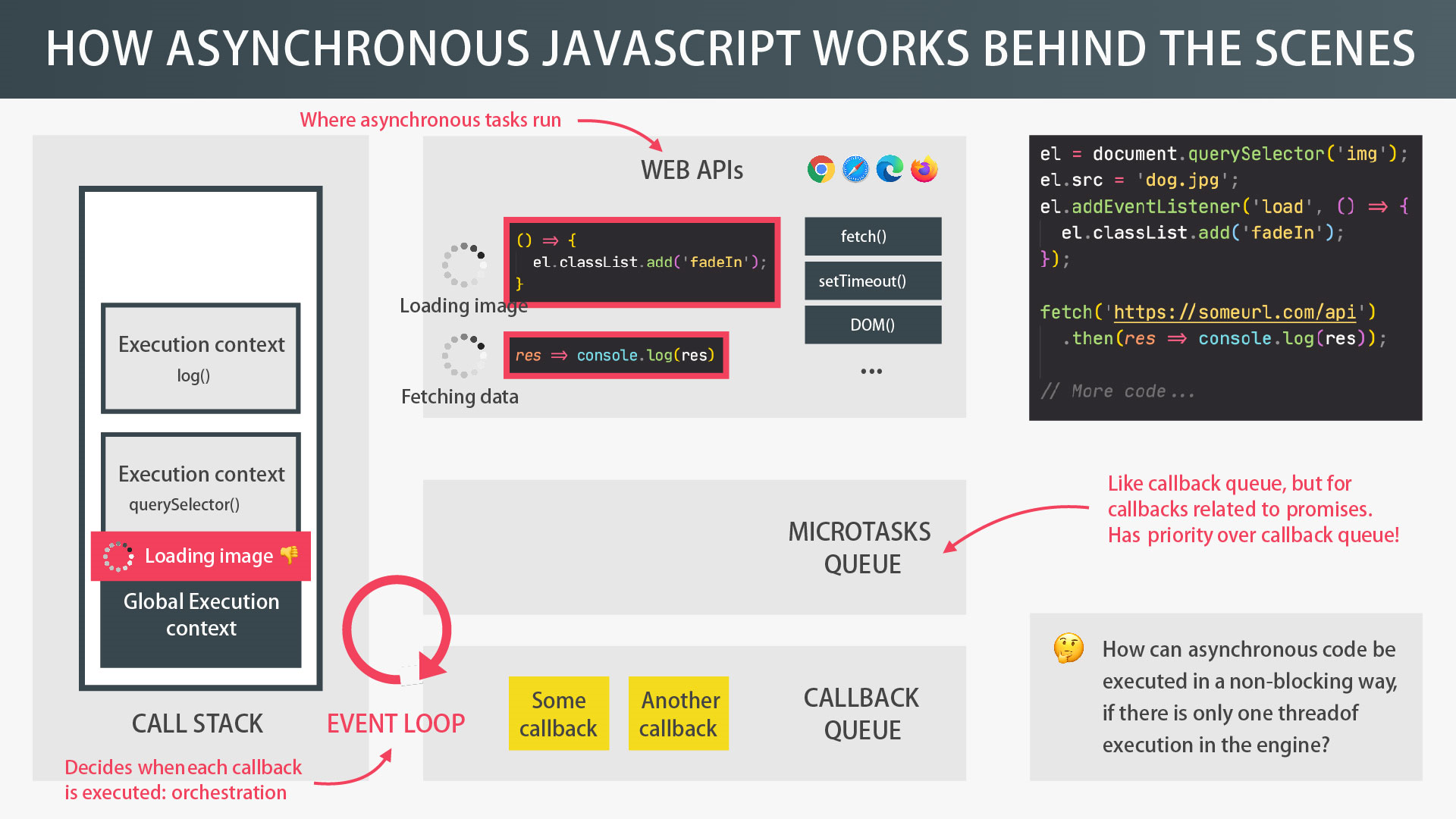
Await/Async function
- Async functions always return a promise
- Comparision to Promise.resolve()
const p = new Promise((res, rej) => {
res(() => console.log("hello world!"));
});
function basicReturn() {
return Promise.resolve(p);
}
async function asyncReturn() {
return p;
}
console.log(p); // Returns a fulfilled Promise
console.log(basicReturn()); // Returns a fulfilled Promise
console.log(asyncReturn()); // Returns a pending Promise
console.log(p === basicReturn()); // true, since "basicReturn" returns a new promise that is resolved with the same value as p
console.log(p === asyncReturn()); // false, because asyncReturn returns the promise p directly, without creating a new promise
Promise.resolve(p).then((f) => f()); //hello world!
Promise.reject(new Error("Problem!")).catch((err) => console.error(err.message)); //Problem!const p = new Promise((res, rej) => {
res(() => console.log("hello world!"));
});
function basicReturn() {
return Promise.resolve(p);
}
async function asyncReturn() {
return p;
}
console.log(p); // Returns a fulfilled Promise
console.log(basicReturn()); // Returns a fulfilled Promise
console.log(asyncReturn()); // Returns a pending Promise
console.log(p === basicReturn()); // true, since "basicReturn" returns a new promise that is resolved with the same value as p
console.log(p === asyncReturn()); // false, because asyncReturn returns the promise p directly, without creating a new promise
Promise.resolve(p).then((f) => f()); //hello world!
Promise.reject(new Error("Problem!")).catch((err) => console.error(err.message)); //Problem!Immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE)
- A function that runs the moment it is invoked or called in the JavaScript event loop
Running Promises in Parallel
- Promise.all
const promise1 = fetchJSON(countryUrl + `/name/${c1}`);
const promise2 = fetchJSON(countryUrl + `/name/${c2}`);
const promise3 = fetchJSON(countryUrl + `/name/${c3}`);
const promiseArr = await Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3]);
//If one promise rejected, all promises get rejectedconst promise1 = fetchJSON(countryUrl + `/name/${c1}`);
const promise2 = fetchJSON(countryUrl + `/name/${c2}`);
const promise3 = fetchJSON(countryUrl + `/name/${c3}`);
const promiseArr = await Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3]);
//If one promise rejected, all promises get rejected- Promise.race:
Shortcircuit when enver the first promise get settled(no matter fufilled or rejected) - Promise.allSettled:
Return all promises whether the promise resolved or rejected - Promise.any:
return first sucessful/resolved promise(ignore rejected promise) then shortcircuited
Modules
- Why modules?
- Compose software:
modules are small building blocks to build complex applications - Isolate components:
modules can be implemented in isolation without thinking the entire codebase - Abstract code:
implement low-level code in modules and import these abstractions into other modules - Orgnized code
- Reuse code:
easy to reuse the same code, even across multiple projects
ES6 Modules
- Modules stored in files, exactly 1 module per file.
- ES6 Module vs Script:
| ES6 Module | Script | |
|---|---|---|
| Top-level variables | Scoped to module | Global |
| Default mode | Strict mode | "Sloppy" mode |
| Top-level "this" | undefined | window |
| Imports and Exports | Support (Need to happen at top-level, Imports are hoisted) | Not support |
Export and Import
Default export vs Named export
- Default export in the export module
export default function(){}
//or
export default variableexport default function(){}
//or
export default variable- To import a Default export module
import yourDefineName from './PathToExportModule.js'
import yourDefineName from './PathToExportModule.js'- Named export in export module
export {variable1,variable2 as yourDefinedName};
export const functionToExport = function(){};export {variable1,variable2 as yourDefinedName};
export const functionToExport = function(){};- To import a Named export module
//Import specific part
import {nameOfTheVariable,nameOfTheFunction as yourDefinedName} from './PathToExportModule.js'
//Import the whole module as an Object
import * as YourDefinedModuleName from './PathToExportModule.js' //Import specific part
import {nameOfTheVariable,nameOfTheFunction as yourDefinedName} from './PathToExportModule.js'
//Import the whole module as an Object
import * as YourDefinedModuleName from './PathToExportModule.js' Top-level await in modules
- From ES2022
<script type="module" defer src="script.js"></script>// Only works when the .js file linked as a module
<script type="module" defer src="script.js"></script>// Only works when the .js file linked as a module//NO need to be in an Async function in this case
const res = await fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts'); //This will block the afterwards code
const data = await res.json();
console.log(data);//NO need to be in an Async function in this case
const res = await fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts'); //This will block the afterwards code
const data = await res.json();
console.log(data);- The blocking code ( await ) in a exporting module, Will also influence the importing module using this exporting module
The Module Pattern (Old)
- closures of IIFE
Common JS ( for NodeJS )
//Export
export.myFunction = function(){}
//Import
const {myFunction} = require('./PathToExportModule.js')//Export
export.myFunction = function(){}
//Import
const {myFunction} = require('./PathToExportModule.js')NPM
npm -v #9.6.6 npm init #Initialize package.json npm install lodash-es #Install ES Module based Lodash npm install parcel --save-dev #Install parcel only as development dependency npm start #same to npm run start npm run build #parcel/webpack build npm install #Will install all the package dependencies written in package.json sudo npm uninstall npm -g #Uninstall npm
npm -v #9.6.6
npm init #Initialize package.json
npm install lodash-es #Install ES Module based Lodash
npm install parcel --save-dev #Install parcel only as development dependency
npm start #same to npm run start
npm run build #parcel/webpack build
npm install #Will install all the package dependencies written in package.json
sudo npm uninstall npm -g #Uninstall npmDon't include the node_modules folder when copy or upload(which will be huge)
Package.json
{
"name": "forkify",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Recipe App",
"main": "index.js",//The main field is a module ID that is the primary entry point to your program. That is, if your package is named foo, and a user installs it, and then does require("foo"), then your main module's exports object will be returned.This should be a module relative to the root of your package folder.For most modules, it makes the most sense to have a main script and often not much else.
//If main is not set, it defaults to index.js in the package's root folder.
"scripts": {
"start": "parcel index.html",
"build": "parcel build index.html --dist-dir ./dist",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "Ken",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@parcel/transformer-sass": "^2.9.3",
"parcel": "^2.9.3",
"process": "^0.11.10"
},
"dependencies": {
"core-js": "^3.31.0",
"fractional": "^1.0.0",
"regenerator-runtime": "^0.13.11"
}
}{
"name": "forkify",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Recipe App",
"main": "index.js",//The main field is a module ID that is the primary entry point to your program. That is, if your package is named foo, and a user installs it, and then does require("foo"), then your main module's exports object will be returned.This should be a module relative to the root of your package folder.For most modules, it makes the most sense to have a main script and often not much else.
//If main is not set, it defaults to index.js in the package's root folder.
"scripts": {
"start": "parcel index.html",
"build": "parcel build index.html --dist-dir ./dist",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "Ken",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@parcel/transformer-sass": "^2.9.3",
"parcel": "^2.9.3",
"process": "^0.11.10"
},
"dependencies": {
"core-js": "^3.31.0",
"fractional": "^1.0.0",
"regenerator-runtime": "^0.13.11"
}
}Lodash
//deepClone
import cloneDeep from './node_modules/lodash-es/cloneDeep.js';
const state = {
cart: [
{ product: 'bread', quantity: 5 },
{ product: 'pizza', quantity: 3 },
],
user: { loggedIn: true },
};
const stateClone = Object.assign({}, state);
const stateDeepClone = cloneDeep(state);
state.user.loggedIn = false;
console.log(stateClone.user.loggedIn); //Also changed to false
console.log(stateDeepClone.user.loggedIn); //Remained to be true//deepClone
import cloneDeep from './node_modules/lodash-es/cloneDeep.js';
const state = {
cart: [
{ product: 'bread', quantity: 5 },
{ product: 'pizza', quantity: 3 },
],
user: { loggedIn: true },
};
const stateClone = Object.assign({}, state);
const stateDeepClone = cloneDeep(state);
state.user.loggedIn = false;
console.log(stateClone.user.loggedIn); //Also changed to false
console.log(stateDeepClone.user.loggedIn); //Remained to be trueArchitecture
- Model,View,Controller(MVC Architecture)
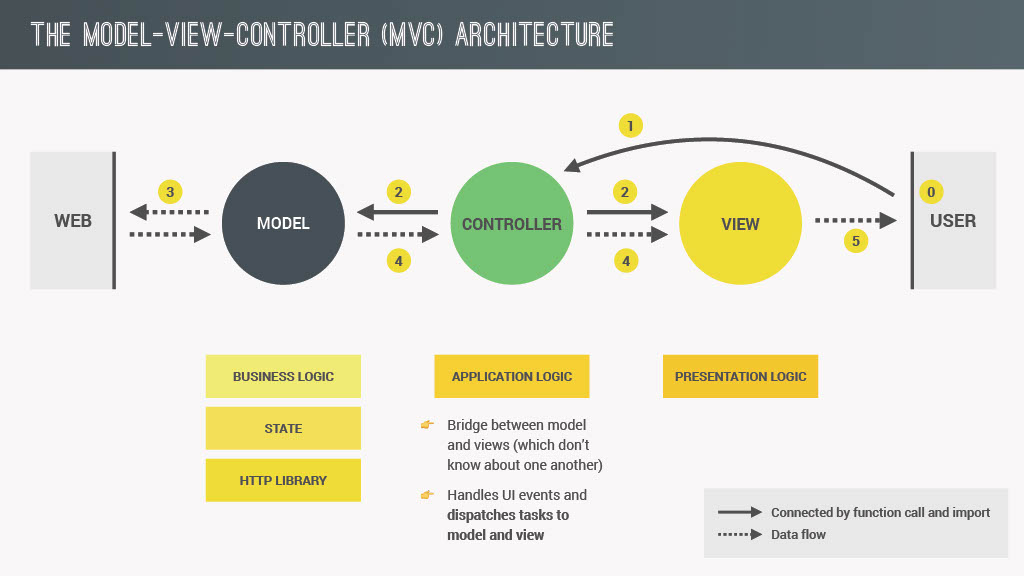
- Components of any architecture
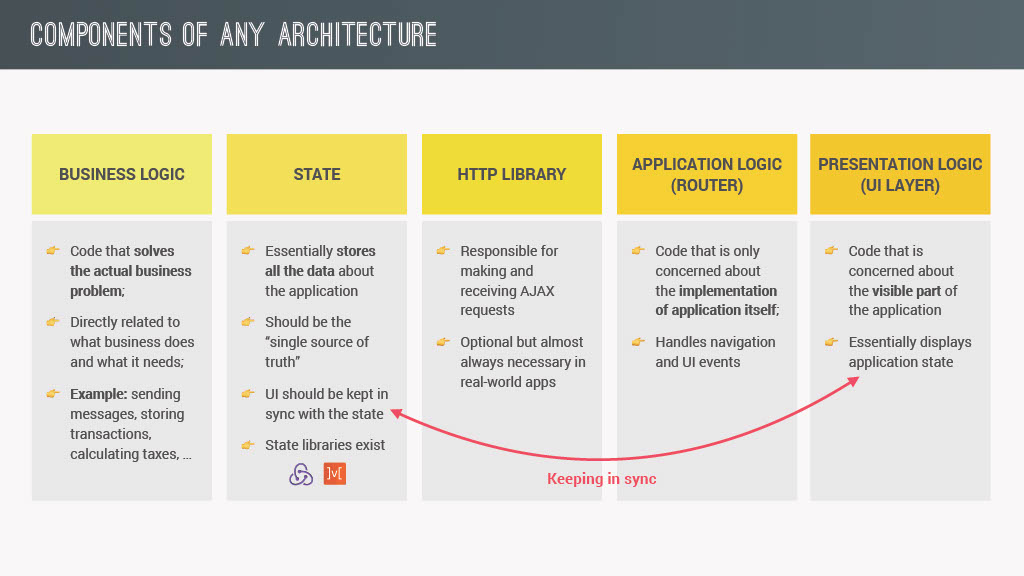
Event Handling in MVC: Publisher-Subscriber Pattern
- Events should be handled in the controller(otherwise we would have application logic in the view)
- Events should be listened for in the view(otherwise we would need DOM elements in the controller)
Debug
Javascript built-in Objects
Date
const today = new Date(); console.log(today); //Mon Jul 17 2023 19:10:58 GMT-0400 (Eastern Daylight Time) const year = today.getFullYear(); const month = today.getMonth(); const date = today.getDate(); const day = today.getDay(); console.log(year, month, date, day); //2023 6 17 1 console.log(today.toDateString()); //Mon Jul 17 2023 let count = 1; const tomorrow = new Date(); tomorrow.setDate(today.getDate() + count); console.log(tomorrow.toDateString()); //Tue Jul 18 2023 count = -1; const yesterday = new Date(); yesterday.setDate(today.getDate() + count); console.log(yesterday.toDateString()); //Sun Jul 16 2023
const today = new Date();
console.log(today); //Mon Jul 17 2023 19:10:58 GMT-0400 (Eastern Daylight Time)
const year = today.getFullYear();
const month = today.getMonth();
const date = today.getDate();
const day = today.getDay();
console.log(year, month, date, day); //2023 6 17 1
console.log(today.toDateString()); //Mon Jul 17 2023
let count = 1;
const tomorrow = new Date();
tomorrow.setDate(today.getDate() + count);
console.log(tomorrow.toDateString()); //Tue Jul 18 2023
count = -1;
const yesterday = new Date();
yesterday.setDate(today.getDate() + count);
console.log(yesterday.toDateString()); //Sun Jul 16 2023Math
Math.floor() Math.round() Math.abs() Math.min(arr) Math.max(arr)
Math.floor()
Math.round()
Math.abs()
Math.min(arr)
Math.max(arr)String
- String.prototype.localeCompare()
//The localeCompare() method returns a number indicating whether a reference string comes before, or after, or is the same as the given string in sort order.
// Returns negative INT if a < b in a.localeCompare(b)
console.log("a".localeCompare("c")); //-1
console.log("check".localeCompare("against")); //1
console.log("a".localeCompare("a")); //0
//The localeCompare() method returns a number indicating whether a reference string comes before, or after, or is the same as the given string in sort order.
// Returns negative INT if a < b in a.localeCompare(b)
console.log("a".localeCompare("c")); //-1
console.log("check".localeCompare("against")); //1
console.log("a".localeCompare("a")); //0
Array
- Array.from
Creates an array from an iterable object.
Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x + x)
// Expected output: Array [2, 4, 6]
Array.from({ length: 5 }, (_, i) => (<span>Number{i + 1}</span>))
// Expected output: Array [Number1,Number2,...Number5]Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x + x)
// Expected output: Array [2, 4, 6]
Array.from({ length: 5 }, (_, i) => (<span>Number{i + 1}</span>))
// Expected output: Array [Number1,Number2,...Number5]